Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy

Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint.
The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, “arthro” (joint) and “skopein” (to look). The term literally means “to look within the joint.” During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your joint. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments.
Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions (cuts), rather than the larger incision needed for standard, open surgery. This results in less pain for patients, and shortens the time it takes to recover and return to favorite activities.
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY
What Is Knee Arthroscopy?
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical technique that can diagnose and treat problems in the knee joint.
Arthroscopy diagnoses several knee problems, such as a torn meniscus or a misaligned patella (kneecap). It can also repair the ligaments of the joint. There are limited risks to the procedure and the outlook is good for most patients. Your recovery time and prognosis will depend on the severity of the knee problem and the complexity of the required procedure.

 What Is Knee Arthroscopy?
What Is Knee Arthroscopy?

What Is Knee Arthroscopy?
Your doctor may recommend that you undergo a knee arthroscopy if you’re experiencing knee pain. Your doctor might have already diagnosed the condition causing your pain, or they may order the arthroscopy to help find a diagnosis. In either case, an arthroscopy is a useful way for doctors to confirm the source of knee pain and treat the problem.
Arthroscopic surgery can diagnose and treat knee injuries, including:
 torn anterior or posterior cruciate ligaments
torn anterior or posterior cruciate ligaments  torn meniscus (the cartilage between the bones in the knee)
torn meniscus (the cartilage between the bones in the knee)  patella that’s out of position
patella that’s out of position  pieces of torn cartilage that are loose in the joint
pieces of torn cartilage that are loose in the joint  removal of a Baker’s cyst
removal of a Baker’s cyst  fractures in the knee bones
fractures in the knee bones  swollen synovium (the lining in the joint)
swollen synovium (the lining in the joint)  HOW DO I PREPARE FOR KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
HOW DO I PREPARE FOR KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
Your doctor or surgeon will advise you how to prepare for your surgery. Be sure to tell them about any prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, or supplements that you’re currently taking. You may need to stop taking certain medicines, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, for weeks or days before the procedure.
You must also refrain from eating or drinking for six to 12 hours before the surgery. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe you a pain medication for any discomfort you experience after the surgery. You should fill this prescription ahead of time so that you have it ready after the procedure.

 WHAT HAPPENS DURING A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
WHAT HAPPENS DURING A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?

Your doctor will give you an anesthetic before your knee arthroscopy. This may be:
 Local (Numbs Your Knee Only)
Local (Numbs Your Knee Only)  Regional (Numbs You From The Waist Down)
Regional (Numbs You From The Waist Down)  General (Puts You Completely To Sleep)
General (Puts You Completely To Sleep)
If you’re awake, you may be able to watch the procedure on a monitor. The surgeon will begin by making a few small incisions, or cuts, in your knee. Sterile salt water, or saline, will then pump in to expand your knee. This makes it easier for the surgeon to see inside the joint. The arthroscope enters one of the cuts and the surgeon will look around in your joint using the attached camera. The surgeon can see the images produced by the camera on the monitor in the operating room. When the surgeon locates the problem in your knee, they may then insert small tools into the incisions to correct the issue. After the surgery, the surgeon drains the saline from your joint and closes your cuts with stitches.
 WHAT ARE THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
WHAT ARE THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
There are risks associated with any type of surgery, though they are rare. Every surgery has the following risks:
 Excessive Bleeding During The Procedure
Excessive Bleeding During The Procedure  Infection At The Site Of The Surgery
Infection At The Site Of The Surgery  Breathing Difficulties Caused By Anesthesia
Breathing Difficulties Caused By Anesthesia  Allergic Reaction To Anesthesia Or Other Medications Administered During Surgery
Allergic Reaction To Anesthesia Or Other Medications Administered During Surgery
There are also risks specific to a knee arthroscopy, such as:
 Bleeding Inside The Knee Joint
Bleeding Inside The Knee Joint  Formation Of A Blood Clot In The Leg
Formation Of A Blood Clot In The Leg  Infection Inside The Joint
Infection Inside The Joint  Stiffness In The Knee
Stiffness In The Knee  Injury Or Damage To The Cartilage, Ligaments, Meniscus, Blood Vessels, Or Nerves Of The Knee
Injury Or Damage To The Cartilage, Ligaments, Meniscus, Blood Vessels, Or Nerves Of The Knee  WHAT IS RECOVERY LIKE AFTER A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?
WHAT IS RECOVERY LIKE AFTER A KNEE ARTHROSCOPY ?

This surgery isn’t very invasive. For most people, the procedure takes less than an hour depending on the specific procedure. You will likely go home on the same day for recovery. You should use an ice pack on your knee and a dressing. The ice will help reduce swelling and minimize your pain.
At home, you should have someone look after you, at least for the first day. Try to keep your leg elevated and put ice on it for a day or two to reduce swelling and pain. You’ll also need to change your dressing. Your doctor or surgeon will tell you when to do these things and for how long. You will probably need to see your surgeon for a follow-up appointment a few days after the procedure.
Your doctor will give you an exercise regimen to follow at home to help your knee recover, or will recommend a physical therapist to see until you’re able to use your knee normally. The exercises are necessary to help restore your full range of motion and to strengthen your muscles. With the proper care, your outlook after having this procedure is excellent.
 SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
Your shoulder is a complex joint that is capable of more motion than any other joint in your body. It is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
Normal anatomy of the shoulder

Ball and socket
The head of your upper arm bone fits into a rounded socket in your shoulder blade. This socket is called the glenoid. A slippery tissue called articular cartilage covers the surface of the ball and the socket. It creates a smooth, frictionless surface that helps the bones glide easily across each other.
The glenoid is ringed by strong fibrous cartilage called the labrum. The labrum forms a gasket around the socket, adds stability, and cushions the joint.

Shoulder capsule
The joint is surrounded by bands of tissue called ligaments. They form a capsule that holds the joint together. The undersurface of the capsule is lined by a thin membrane called the synovium. It produces synovial fluid that lubricates the shoulder joint.

Rotator cuff
Four tendons surround the shoulder capsule and help keep your arm bone centered in your shoulder socket. This thick tendon material is called the rotator cuff. The cuff covers the head of the humerus and attaches it to your shoulder blade.

Bursa
There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the rotator cuff and the bone on top of your shoulder (acromion). The bursa helps the rotator cuff tendons glide smoothly when you move your arm.
 WHEN SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY IS RECOMMENDED ?
WHEN SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY IS RECOMMENDED ?

Your doctor may recommend shoulder arthroscopy if you have a painful condition that does not respond to nonsurgical treatment. Nonsurgical treatment includes rest, physical therapy, and medications or injections that can reduce inflammation. Inflammation is one of your body’s normal reactions to injury or disease. In an injured or diseased shoulder joint, inflammation causes swelling, pain, and stiffness.
Injury, overuse, and age-related wear and tear are responsible for most shoulder problems. Shoulder arthroscopy may relieve painful symptoms of many problems that damage the rotator cuff tendons, labrum, articular cartilage, and other soft tissues surrounding the joint.

Common arthroscopic procedures include:
- Rotator cuff repair
- Bone spur removal
- Removal or repair of the labrum
- Repair of ligaments
- Removal of inflamed tissue or loose cartilage
- Repair for recurrent shoulder dislocation

Less common procedures such as nerve release, fracture repair, and cyst excision can also be performed using an arthroscope. Some surgical procedures, such as shoulder replacement, still require open surgery with more extensive incisions.
 PLANNING FOR SURGERY
PLANNING FOR SURGERY
Your orthopaedic surgeon may ask you to see your primary doctor to make sure that you do not have any medical problems that need to be addressed before your surgery. Blood tests, an electrocardiogram, or chest x-ray may be needed to safely perform your surgery.
If you have certain health risks, a more extensive evaluation may be necessary before your surgery. Be sure to inform your orthopaedic surgeon of any medications or supplements that you take. You may need to stop taking some of these prior to surgery.
If you are generally healthy, your arthroscopy will most likely be performed as an outpatient. This means you will not need to stay overnight at the hospital. The hospital or surgery center will contact you ahead of time to provide specific details about your procedure. Make sure to follow the instructions on when to arrive and especially on when to stop eating or drinking prior to your surgery.


Before the operation, a member of the anesthesia staff will talk with you about anesthesia options. Shoulder arthroscopy is most commonly performed using regional nerve blocks which numb your shoulder and arm. This numbing medicine is injected in the base of your neck or high on your shoulder. This is where the nerves that control feeling in your shoulder and arm are located. In addition to its use as an anesthetic during surgery, a nerve block will help control pain for a few hours after the surgery is completed. Many surgeons combine nerve blocks with sedation or a light general anesthetic because patients can become uncomfortable staying in one position for the length of time needed to complete the surgery.
Most arthroscopic procedures take less than an hour, however, the length of your surgery will depend on what your surgeon finds and what repairs are required.
 SURGICAL PROCEDURE
SURGICAL PROCEDURE

Positioning and Preparation
Once in the operating room, you will be positioned so that your surgeon can easily adjust the arthroscope to have a clear view of the inside of your shoulder. The two most common patient positions for arthroscopic shoulder surgery are:
- Beach chair position. This is a semi-seated position similar to sitting in a reclining chair.
- Lateral decubitius position. In this position the patient lies on his or her side on an operating table.
Each position has some slight advantages. Surgeons select positions based on the procedure being performed, as well as their individual training.
Once you are positioned, the surgical team will remove hair, if needed, and then spread an antiseptic solution over your shoulder to clean the skin. They will cover your shoulder and arm with sterile drapes, and will most likely place your forearm in a holding device to ensure your arm stays still.

Procedure
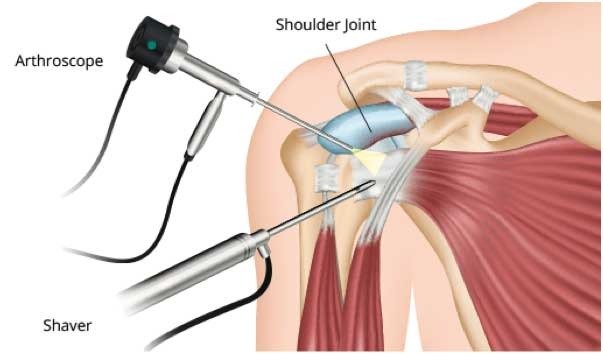
Your surgeon will first inject fluid into the shoulder to inflate the joint. This makes it easier to see all the structures of your shoulder through the arthroscope. Then your surgeon will make a small puncture in your shoulder (about the size of a buttonhole) for the arthroscope. Fluid flows through the arthroscope to keep the view clear and control any bleeding. Images from the arthroscope are projected on the video screen showing your surgeon the inside of your shoulder and any damage.
Once the problem is clearly identified, your surgeon will insert other small instruments through separate incisions to repair it. Specialized instruments are used for tasks like shaving, cutting, grasping, suture passing, and knot tying. In many cases, special devices are used to anchor stitches into bone.(Left) A rotator cuff tear. (Right) The rotator cuff tendon has been re-attached to the humeral head with sutures.
Your surgeon may close your incisions with stitches or steri-strips (small Band-Aids) and cover them with a large, soft bandage.
 RECOVERY
RECOVERY
Postoperative – After surgery, you will stay in the recovery room for 1 to 2 hours before being discharged home. Nurses will monitor your responsiveness and provide pain medication, if needed. You will need someone to drive you home and stay with you for at least the first night.

At Home
Although recovery from arthroscopy is often faster than recovery from open surgery, it may still take weeks for your shoulder joint to completely recover.
You can expect some pain and discomfort for at least a week after surgery. If you have had a more extensive surgery, however, it may take several weeks before your pain subsides. Ice will help relieve pain and swelling. Your doctor may prescribe pain medicine, if needed.
Many types of pain medication are available to help control pain, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and local anesthetics. Treating pain with medications can help you feel more comfortable, which will help your body heal faster and recover from surgery faster.
Opioids can provide excellent pain relief, however, they are a narcotic and can be addictive. It is important to use opioids only as directed by your doctor. You should stop taking these medications as soon as your pain starts to improve.
Although it does not affect how your shoulder heals, lying flat may pull on your shoulder and cause discomfort. Some patients are more comfortable sleeping in a reclining chair or propped up in bed during the first days after surgery.
A few days after surgery, you should be able to replace your large bandage with simple Band-Aids. You may shower once your wounds are no longer draining, but try not to soak or scrub your incisions.
You will most likely need a sling or special immobilizer to protect your shoulder. Your surgeon will discuss with you how long the sling will be needed.


REHABILITATION
Rehabilitation plays an important role in getting you back to your daily activities. An exercise program will help you regain shoulder strength and motion. Your surgeon will develop a rehabilitation plan based on the surgical procedures you required.
If you have had a more complicated surgical repair, your surgeon may recommend a physical therapist to supervise your exercise program.It is important that you make a strong effort at rehabilitation in order for your surgery to succeed.

COMPLICATIONS
Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. As with any surgery, however, there are some risks. These are usually minor and treatable. Potential problems with arthroscopy include infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, and damage to blood vessels or nerves.
Your surgeon will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation.

LONG-TERM OUTCOMES
Because patients have varied health conditions, complete recovery time is different for everyone. If you have had a minor repair, you may not need a sling and your strength may return after a short period of rehabilitation. You may be able to return to work or school within a few days of your procedure.
It takes longer to recover from more complicated procedures. Although the incisions are small in arthroscopy, extensive damage within the joint can be repaired with the procedure. Full recovery may take several months. Although it can be a slow process, following your surgeon’s guidelines and rehabilitation plan is vital to a successful outcome.
