Sports Injuries
Sports Injuries
 EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT SPORTS INJURIES AND REHAB
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT SPORTS INJURIES AND REHAB

Overview
Sports injuries occur during exercise or while participating in a sport. Children are particularly at risk for these types of injuries, but adults can get them, too.
You’re at risk for sports injuries if you :
- Haven’t Been Regularly Active
- Don’t Warm Up Properly
- Before Exercise
- Play Contact Sports
Read on to learn more about sports injuries, your treatment options, and tips for preventing them in the first place.
 TYPES OF SPORTS INJURIES
TYPES OF SPORTS INJURIES
Different sports injuries produce different symptoms and complications. The most common types of sports injuries include:
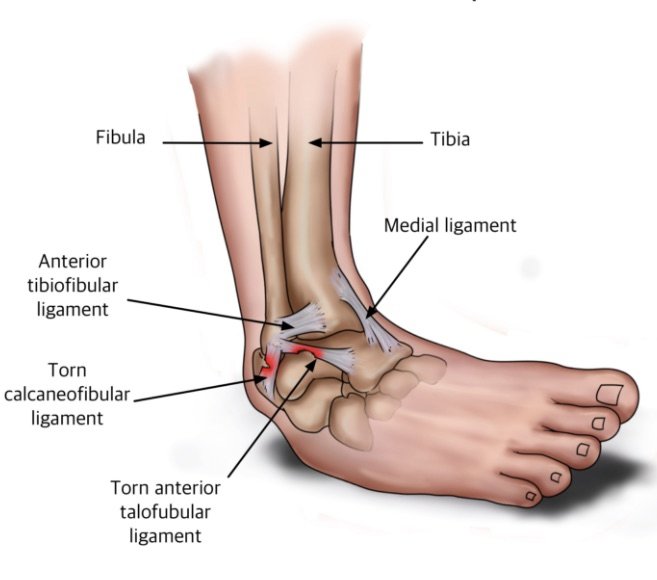
Sprains
Overstretching or tearing the ligaments results in a sprain. Ligaments are pieces of tissue that connect two bones to one another in a joint.

Knee injuries
Any injury that interferes with how the knee joint moves could be a sports injury. It could range from an overstretch to a tear in the muscles or tissues in the knee.

Swollen muscles
Swelling is a natural reaction to an injury. Swollen muscles may also be painful and weak.

Fractures
Bone fractures are also known as broken bones.

Strains
Overstretching or tearing muscles or tendons results in a sprain. Tendons are thick, fibrous cords of tissue that connect bone to muscle. Strains are commonly mistaken for sprains. Here’s how tell them apart.

Achilles tendon rupture.
The Achilles tendon is a thin, powerful tendon at the back of your ankle. During sports, this tendon can break or rupture. When it does, you may experience sudden, severe pain and difficulty walking.

Dislocations
Sports injuries may dislocate a bone in your body. When that happens, a bone is forced out of its socket. This can be painful and lead to swelling and weakness.

Rotator cuff injury
Four pieces of muscle work together to form the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff keeps your shoulder moving in all directions. A tear in any of these muscles can weaken the rotator cuff.
Sports injuries are injuries that occur when engaging in sports or exercise. Sports injuries can occur due to overtraining, lack of conditioning, and improper form or technique. Failing to warm up increases the risk of sports injuries. Bruises, strains, sprains, tears, and broken bones can result from sports injuries. Soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, tendons, fascia, and bursae may be affected. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is another potential type of sports injury.
Pulled Muscle
Torn ACL
Torn MCL
Shin Splints
Stress Fracture
Plantar Fasciitis
Sprained Ankle
Tennis Elbow
Pulled Muscle
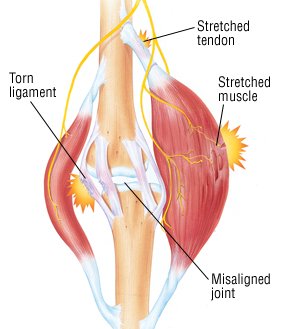 Muscle strain is another name for a pulled muscle. It occurs when a muscle is overstretched and tears. Symptoms of a pulled muscle may include pain, swelling, weakness, and difficulty or inability to use the muscle. Muscles in the quadriceps, the calves, hamstrings, groin, low back, and shoulder are the most common sites for pulled muscles.
Minor muscle strains resolve with RICE — Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help manage pain and swelling as well. More serious muscle strains require evaluation and treatment by a doctor.
Muscle strain is another name for a pulled muscle. It occurs when a muscle is overstretched and tears. Symptoms of a pulled muscle may include pain, swelling, weakness, and difficulty or inability to use the muscle. Muscles in the quadriceps, the calves, hamstrings, groin, low back, and shoulder are the most common sites for pulled muscles.
Minor muscle strains resolve with RICE — Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help manage pain and swelling as well. More serious muscle strains require evaluation and treatment by a doctor.Torn ACL
 The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) helps hold the knee joint together and provides stability. A torn ACL is a sports injury that may occur when landing the wrong way, changing direction or stopping quickly, or from a direct blow to the knee. People who suffer a torn ACL may hear a pop and then feel their knee no longer functions. Pain, swelling, and loss of range of motion are symptoms of a torn ACL.
It may be difficult to walk. A torn ACL needs to be reconstructed surgically, usually using a graft from another ligament in the patient’s own body. Significant rehabilitation is necessary to restore the strength and function of the knee joint after surgery. Depending on the age, health status, and desired activity level of the patient, some may not elect to have surgery. In that case, braces and physical therapy will not cure the condition, but may provide some relief.
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) helps hold the knee joint together and provides stability. A torn ACL is a sports injury that may occur when landing the wrong way, changing direction or stopping quickly, or from a direct blow to the knee. People who suffer a torn ACL may hear a pop and then feel their knee no longer functions. Pain, swelling, and loss of range of motion are symptoms of a torn ACL.
It may be difficult to walk. A torn ACL needs to be reconstructed surgically, usually using a graft from another ligament in the patient’s own body. Significant rehabilitation is necessary to restore the strength and function of the knee joint after surgery. Depending on the age, health status, and desired activity level of the patient, some may not elect to have surgery. In that case, braces and physical therapy will not cure the condition, but may provide some relief.Torn MCL
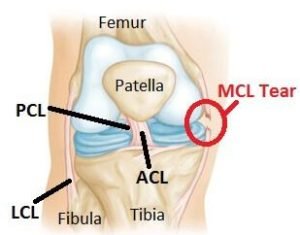 The medial collateral ligament (MCL) connects the upper leg bone (femur) to the larger bone of the lower leg (tibia). It is located on the inner side of the knee. The MCL is typically injured when the knee joint is pushed sideways when making a wrong move or by receiving a direct blow to the knee.
A torn MCL results in pain, swelling, and instability of the joint. The condition is often treated with ice, bracing, and physical therapy. If other structures in the knee are injured or if the torn MCL is severe, surgery may be recommended.
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) connects the upper leg bone (femur) to the larger bone of the lower leg (tibia). It is located on the inner side of the knee. The MCL is typically injured when the knee joint is pushed sideways when making a wrong move or by receiving a direct blow to the knee.
A torn MCL results in pain, swelling, and instability of the joint. The condition is often treated with ice, bracing, and physical therapy. If other structures in the knee are injured or if the torn MCL is severe, surgery may be recommended.Shin Splints
 Shin splints are throbbing, aching, or stabbing pain on the insides of the lower leg. Shin splints are a repetitive use injury that may occur in runners or those who are beginning to exercise. Pain occurs when muscles and tendons around the tibia (the larger of the two lower leg bones) become inflamed.
Stretching, resting, and applying ice can help relieve shin splints. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and swelling. Bandaging the area may help prevent swelling. Flat feet increase the risk of shin splints. Orthotics and proper athletic shoes may offer support and decrease the risk of shin splints.
Shin splints are throbbing, aching, or stabbing pain on the insides of the lower leg. Shin splints are a repetitive use injury that may occur in runners or those who are beginning to exercise. Pain occurs when muscles and tendons around the tibia (the larger of the two lower leg bones) become inflamed.
Stretching, resting, and applying ice can help relieve shin splints. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and swelling. Bandaging the area may help prevent swelling. Flat feet increase the risk of shin splints. Orthotics and proper athletic shoes may offer support and decrease the risk of shin splints.Stress Fracture
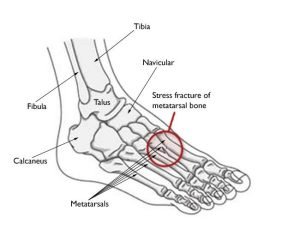 A stress fracture is an overuse injury that occurs when muscles are no longer able to absorb the impact from physical activity, and a bone absorbs the pressure, resulting in a break. Stress fractures can occur when increasing activity, especially too quickly. The majority of stress fractures occur in the lower legs and feet.
Women are more prone to stress fractures than men. Stress fractures cause pain with activity. Rest is prescribed to allow a stress fracture to heal. Sometimes a special shoe or a brace helps decrease stress on the bone, which facilitates healing.
A stress fracture is an overuse injury that occurs when muscles are no longer able to absorb the impact from physical activity, and a bone absorbs the pressure, resulting in a break. Stress fractures can occur when increasing activity, especially too quickly. The majority of stress fractures occur in the lower legs and feet.
Women are more prone to stress fractures than men. Stress fractures cause pain with activity. Rest is prescribed to allow a stress fracture to heal. Sometimes a special shoe or a brace helps decrease stress on the bone, which facilitates healing.Plantar Fasciitis
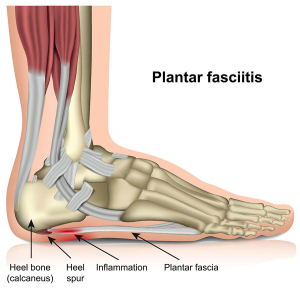 The plantar fascia is a ligament that connects the heel to the front of the foot, supporting the arch. Plantar fasciitis is inflammation of this ligament. It causes heel pain often felt the first thing in the morning after getting out of bed or after being active. Stress and strain on the feet increases the risk of plantar fasciitis. Obesity, tight calf muscles, repetitive use, high arches, and new athletic activities are all risk factors for this condition.
Plantar fasciitis is treated with rest, ice, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and special stretching exercises. Cushioning insoles may provide relief. Wearing splints at night may help decrease pain. More severe cases of plantar fasciitis may be treated with cortisone injections, physical therapy, and surgery.
The plantar fascia is a ligament that connects the heel to the front of the foot, supporting the arch. Plantar fasciitis is inflammation of this ligament. It causes heel pain often felt the first thing in the morning after getting out of bed or after being active. Stress and strain on the feet increases the risk of plantar fasciitis. Obesity, tight calf muscles, repetitive use, high arches, and new athletic activities are all risk factors for this condition.
Plantar fasciitis is treated with rest, ice, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and special stretching exercises. Cushioning insoles may provide relief. Wearing splints at night may help decrease pain. More severe cases of plantar fasciitis may be treated with cortisone injections, physical therapy, and surgery.Sprained Ankle
 A sprained ankle occurs when the ligaments that support the joint become overstretched. Ankle sprains may occur when playing sports or doing everyday activities. Stepping wrong on an uneven surface or stepping in a way that twists or rolls the foot may lead to an ankle sprain.
Sprains and the pain they cause may range from mild to severe. RICE — rest, ice, compression, and elevation — are used to treat ankle sprains. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and swelling. Severe sprains may require a brace or cast for several weeks to facilitate healing.
A sprained ankle occurs when the ligaments that support the joint become overstretched. Ankle sprains may occur when playing sports or doing everyday activities. Stepping wrong on an uneven surface or stepping in a way that twists or rolls the foot may lead to an ankle sprain.
Sprains and the pain they cause may range from mild to severe. RICE — rest, ice, compression, and elevation — are used to treat ankle sprains. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and swelling. Severe sprains may require a brace or cast for several weeks to facilitate healing.Tennis Elbow
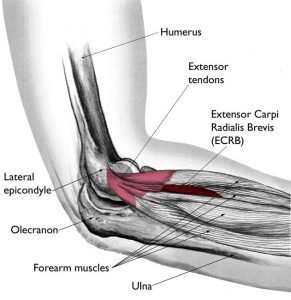 Tennis elbow is an overuse injury that may be associated with playing racket sports. Plumbers, painters and those in similar professions are also at risk. Tennis elbow involves inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow caused by small tears. Tennis elbow causes pain and may be associated with a weak grip. Rest and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate tennis elbow symptoms.
Wearing a special brace on the forearm may help decrease pressure on the sore area. Physical therapy may be helpful. Steroid injections can decrease inflammation. Surgery may be an option for tennis elbow when other treatments have failed.
Tennis elbow is an overuse injury that may be associated with playing racket sports. Plumbers, painters and those in similar professions are also at risk. Tennis elbow involves inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow caused by small tears. Tennis elbow causes pain and may be associated with a weak grip. Rest and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate tennis elbow symptoms.
Wearing a special brace on the forearm may help decrease pressure on the sore area. Physical therapy may be helpful. Steroid injections can decrease inflammation. Surgery may be an option for tennis elbow when other treatments have failed.
Low Back Pain
There are many causes of low back pain. Back pain may be due to overuse, such as playing one too many rounds of golf or lifting heavy weights. This kind of back strain usually resolves on its own without treatment. Rest and anti-inflammatory medications can provide relief. Using proper form when exercising and increasing the duration of workouts slowly can help protect the back. In some cases, it may be necessary to modify exercise technique or perform daily activities in a different way in order to reduce the risk of back injury. Other causes of back pain may be more serious and require medical or surgical intervention.

Runner’s Knee
Runner’s knee – also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome – is a painful condition that occurs when tendons, joint lining (synovia), and/or other soft tissues of the knee become irritated. Overuse can cause runner’s knee. So can a misaligned kneecap. In addition to pain, runner’s knee may lead to popping and cracking. Switching to activities that do not stress knee joints may minimize problems. RICE – rest, ice, compression, and elevation – may help. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy, and orthotics may provide relief. Rarely, surgery may be an option for severe cases that have not responded to other treatments.

Concussion
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occurs when the brain undergoes rapid acceleration inside the skull. A direct hit to the head or body may cause a concussion. People who engage in contact sports like football are at increased risk for concussions. The symptoms often include headache, loss of consciousness, memory loss, sleepiness, nausea, vomiting, and more. A thorough neurological exam is necessary after a concussion to determine the extent of the injury. Healing from a concussion requires rest, both physical and mental, to allow the brain to recover. People who suffer concussions must receive a doctor’s clearance before resuming sports, especially young people whose brains are more vulnerable.

Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is inflammation that causes pain on the lower back of the leg just above the heel. The area may become painful, swollen, and stiff. The pain worsens after physical activity. The tendon may become thickened and, in some cases, bone spurs may develop in the area. Achilles tendonitis may be treated with rest, ice, stretching, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Strengthening exercises prescribed by a physical therapist may help. Special footwear and orthotics can help take the strain off the affected heel
Hip Bursitis
The hip region contains two major bursae. The one located on the outside of the hip is called the trochanteric bursa. The other is called the ischial bursa which covers the ischial tuberosity, more commonly known as the sits bones. Inflammation of either bursae may lead to stiffness and pain around the hip joint not to be confused with the true joint pain of arthritis. Overuse from running, cycling, and similar activities can lead to hip bursitis. The condition causes hip pain that tends to be worse at night. Getting up from a seated position may cause pain. Treatment of hip bursitis consists of avoiding activities that produce symptoms and taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and steroid injections may be warranted. Using a cane or other assistive device may help take the load off the inflamed joint.


Sports Injury Prevention
Physical activity is an important part of maintaining overall health. However, certain precautions should be taken to minimize the risk of sports injuries. Using the correct equipment and maintaining equipment can help prevent sports injuries. Wearing the recommended protective gear can help shield the body against injury. Resting between workouts gives the body time to rest and repair. Starting activity slowly and gradually increasing strength, flexibility, and endurance gives muscles, bones, and other tissues the opportunity to adapt to more difficult workouts, minimizing the risk of injury. Finally, listening to the body and backing off at the first signs of pain, discomfort, stress, or overheating will help reduce the risk of sports injuries
Also take these steps to avoid sports injuries:

Use the proper technique
Learn the proper way to move during your sport or activity. Different types of exercise require different stances and postures. For example, in some sports, bending your knees at the right time can help avoid an injury to your spine or hips.

Don’t overdo it
If you do get hurt, make sure you’re healed before you start the activity again. Don’t try to “work through” the pain.
When you return after letting your body recover, you may need to ease yourself back into the exercise or sport rather than jumping back in at the same intensity.

Resume activity slowly
Don’t be tempted to nurse your injury for too long. Excessive rest may delay healing. After the initial 48-hour period of RICE, you can start using heat to help relax tight muscles. Take things slowly, and ease back in to exercise or your sport of choice.

Have the proper equipment
Wear the right shoes. Make sure you have the proper athletic protection. Ill-fitting shoes or gear can increase your risk for injury.

Cool down
Remember to cool down after your activity. Usually, this involves doing the same stretching and exercises involved in a warmup.
 RISKS
RISKS
Anyone may find themselves coping with a sports injury, regardless of the last time they suited up for the baseball diamond or squared off with a linebacker on the gridiron. But some factors put you or a loved one at an increased risk for injury.

Childhood
Because of their active nature, children are especially at risk for sports injuries. Children often don’t know their physical limits. That means they may push themselves to injury more easily than adults or teenagers.

Age
The older you grow, the more likely you are to experience an injury. Age also increases the odds that you have sports injuries that linger. New injuries may aggravate these previous injuries.

Lack of care
Sometimes, serious injuries start off as small ones. Many injuries that result from overuse, such as tendonitis and stress fractures, can be recognized early by a doctor. If they’re left untreated or ignored, they can develop into a serious injury.

Being overweight
Carrying around extra weight can put unnecessary stress on your joints, including your hips, knees, and ankles. The pressure is magnified with exercise or sports. This increases your risk for sports injury.
Children or adults who plan to begin participating in sports can benefit by having a physical examination by a doctor first.
 DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSIS
There are numerous types of IOL (Intraocular lens) option that we use to replace the original oneMany sports injuries cause immediate pain or discomfort. Others, like overuse injuries, might be noticed only after long-term damage. These injuries are often diagnosed during routine physical examinations or checkups.
If you think you have a sports injury, your doctor will likely use the following steps to get a diagnosis. These include:

PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Your doctor may attempt to move the injured joint or body part. This helps them see how the area is moving, or how it’s not moving if that’s the case.

IMAGING TESTS
This involves asking you questions about how you were injured, what you were doing, what you’ve done since the injury, and more. If this is your first time visiting this doctor, they may also ask for a more thorough medical history.

USE OF CERTAIN MEDICINE
X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds can all help your doctor and healthcare providers see inside your body. This helps them confirm a sports injury diagnosis.
If your doctor suspects you have a sprain or strain, they may recommend you follow the RICE method.
Follow these recommendations and keep an eye on your symptoms. If they get worse, that can mean you have a more serious sports injury.
 CALL YOUR DOCTOR
CALL YOUR DOCTOR

Call your doctor if there are signs of swelling or if it hurts to place weight on the affected area. If the problem is in the location of a previous injury, seek medical attention right away.Contact a healthcare provider if you don’t see any improvement after 24 to 36 hours of RICE.
Because a child’s skeleton isn’t fully developed, the bones are weaker than an adult’s. Take extra precautions with a child’s sports injuries. What looks like a tissue injury may in fact be a more serious fracture.
Don’t ignore your symptoms. Remember, the earlier you get a diagnosis and treatment, the sooner you’ll recover and get back in the game.
